A domain name is a human-readable address that translates into a numerical IP address through the Domain Name System (DNS) — essentially acting as the internet’s phone book. Instead of memorizing IP addresses like “192.168.1.2,” you type a memorable name like “nameexperts.com” into your browser, and DNS routes you to the correct server. Understanding how domain names work is essential for anyone building a website, investing in domains, or acquiring a premium domain for their business. This guide breaks down the three components of a domain name (TLD, second-level domain, subdomain), how ICANN manages the global namespace, and why domain names function as leased assets rather than permanent property.
There aren’t many people today who don’t know what a domain name is – but few actually understand how they really work. In this post, NameExperts.com Director Joe Uddeme explains what’s going on behind the scenes.
A domain name is what you type when you want to visit a website. For example, you type “Google.com” into your web browser, and it takes you directly to Google to search for stuff. But a lot happens behind the scenes to ensure the domain name you type takes you to the correct website.
In fact, it’s all pretty complicated – and interesting, too. If you want to buy a premium domain name worth in the tens or even hundreds of thousands, having clear insight into what you’re actually paying for might be a good idea. This article will explain what happens and demystify how the world of URLs and the web works.
Key takeaways:
- Understanding the different components of a domain name
- Proven ways to buy a domain name
- Domain name facts and FAQs

How A Domain Name Leads You To A Website On the Internet
The Internet is an extensive network of computers connected to each other via cables; each computer on this network can communicate with others. Every computer is identified by a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address, which consists of four numbers separated by periods, e.g., 192.168.1.2.
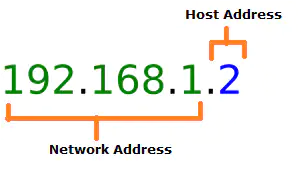
Each website is hosted by a specific computer or server. When you want to visit that website, you need to point to the IP address of the computer hosting it. But IP addresses are difficult to remember. Imagine you had to memorize the unique IP addresses of all the websites you visit; that’ll be impossible, which is why domain names were invented.
A domain name is a human-readable name pointing to a specific IP address on the web. Whenever you type a domain name into your browser, it queries a vast database called the Domain Name System (DNS) and gets the corresponding IP address of the website you want to visit.
The Domain Name System is akin to a phonebook in your home containing your friends’ names and phone numbers. You don’t remember all your friends’ phone numbers; you just need to know their names. Whenever you need a specific number, you check for the name and get it.
This is precisely what the Domain Name System accomplishes; you type a domain, and it gives the correct IP address to your web browser. Your browser fetches the data from the server using that IP address and shows it to you.
Parts Of A Domain Name
A domain name has three main parts: top-level domain (TLD), second-level domain, and subdomain.
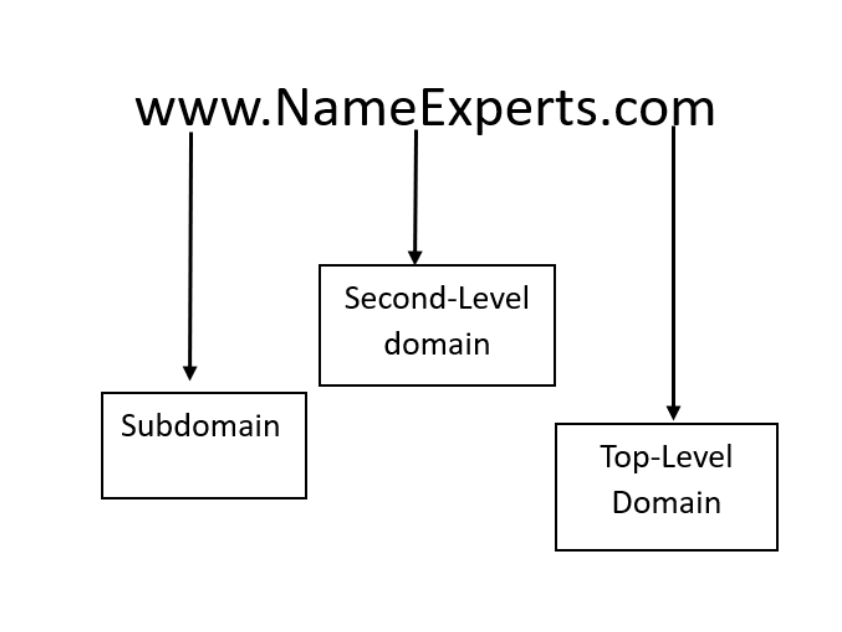
1. Top-Level Domain
The top-level domain (TLD) is the last segment of text in a domain name. The most popular TLDs you should be familiar with include
- .com
- .net
- .co
- .edu
- .org
Yet, there are over 1,500 TLDs you can choose from. A lot of them are assigned to specific countries, such as;
- .uk (United Kingdom)
- .tv (Tuvalu)
- .br (Brazil)
- .ca (Canada)
- .cn (China)
- .de (Germany)
There are many other random TLDs such as .website, .book., .dog, .attorney, and .band. A popular one today is the .ai domain name, which has been a hit with tech companies.
2. Second-level domain (SLD)
This is the middle part of the domain name. It is a unique word or phrase identifying the website you want to visit. This part of the domain plays the biggest role in branding an online business. It’s also important in search engine rankings.
3. Subdomain
A subdomain is the part that comes before the main domain. They are attached to the main domain and separated by a period, e.g., blog.example.com, support.website.com.
Subdomains function like independent websites but are attached to the main site. For instance, you can have an online store or a blog attached to your main business site.
Who Manages the Domain Name System (DNS)
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the agency responsible for managing the global domain name system. It is a nonprofit organization that enacts policies for creating and managing domain names. It permits companies called domain registrars to sell domain names on its behalf.
Technically, you don’t own any domain that you use. You’re leasing it from ICANN (via your domain registrar) and controlling it as long as you renew the registration. If your registration expires, another person can take control of the domain – although with a little effort it’s possible to secure a domain name forever (sort of).
How To Buy A Domain Name
To buy a domain, you can head to any domain registrar’s website and check if someone else has not registered the domain name you want. If so, you can immediately pay for it and start using it.
If the domain name you want has already been registered, don’t fret. You can hire a domain name broker to help you trace, contact the owner, and negotiate a possible purchase. Domain brokers have experience arranging domain sales, so they’ll help you pay a fair price for the domain you want.
Tips For Choosing A Domain Name
- It should be short and simple. Longer domain names are more difficult to remember. Try and choose a strong domain name that will match your business goals and ambitions.
- Avoid using hyphens and numbers in the domain name.
- Use keywords related to your line of business. This helps improve your branding and search rankings.
- A .com TLD should be your first option. If that isn’t available, use other popular TLDs such as .co and .net. The more popular the TLD is, the easier it will be to promote.

Frequently Asked Questions about Domains
How long can I register a domain name for?
The maximum registration period for a domain name is 10 years. But you can renew it every 10 years and keep control of the domain.
What is a premium domain name?
They are high-quality domains that people often buy to flip for a higher price later. Demand for premium domains is high, and the price increases over time, making them good investments.
Can you sell your domain name?
Yes, you can sell your domain name anytime you want to. You can do that yourself or enlist a domain broker to find a buyer for the best price.
How do you find the owner of a domain?
You can identify a domain’s owner by querying the public WHOIS database, which contains contact information about the registered owner of every domain.
What happens if I don’t renew my domain name?
Registrars usually give a 30-day grace period in which you can reclaim the domain. Your domain will be auctioned on the market if that period runs out.
About the author
Joe Uddeme is Director and Principal of Name Experts, one of the world’s leading domain name brokerage services. He has overseen domain name sales and acquisitions totaling more than $150 million and is renowned worldwide as a go-to expert in buying and selling premium domains. Contact us at: [email protected]
Subscribe for More Domain Buying & Selling Advice
Ready to Secure the Perfect Domain for Your Business?
Understanding how domains work is step one. Step two is acquiring the right one. Name Experts helps businesses find and acquire premium domain names that drive growth, build credibility, and dominate search results.
Find Your DomainFrequently Asked Questions
A domain name is a human-readable web address (like google.com or nameexperts.com) that identifies a website on the internet. Behind the scenes, the Domain Name System (DNS) translates this readable name into a numerical IP address that computers use to locate the correct web server. When you type a domain name into your browser, your device queries DNS servers that look up the corresponding IP address and route your connection to the right website. This system means you never need to memorize strings of numbers to visit websites.
A domain name consists of three main components. The top-level domain (TLD) is the extension after the final dot -- like .com, .org, or .ai. The second-level domain (SLD) is the brandable portion before the TLD -- like "nameexperts" in nameexperts.com. Subdomains are optional prefixes like "www" or "blog" that create separate sections of a website (e.g., blog.nameexperts.com). Together, these components form a hierarchical addressing system managed by ICANN and the global DNS infrastructure.
A domain name is the core web address (e.g., nameexperts.com), while a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the complete address that includes the protocol, domain, and specific page path. For example, "https://nameexperts.com/blog/how-does-a-domain-name-work/" is a URL, while "nameexperts.com" is the domain name. The domain identifies the website itself, while the URL points to a specific page or resource within that website.
DNS works like the internet's phone book, translating domain names into IP addresses through a distributed lookup process. When you enter a domain in your browser, your device first checks its local cache for the IP address. If not found, it queries a recursive DNS resolver, which checks root nameservers, TLD nameservers, and authoritative nameservers in sequence until the correct IP address is found. This entire process typically completes in milliseconds, invisibly routing you to the correct website.
The .com extension dominates with over 160 million registrations because of three decades of user conditioning, universal recognition, and brand trust. Consumers have been trained to assume websites end in .com -- many type it automatically or default to it when guessing a company's web address. This ingrained behavior means .com domains generate more direct type-in traffic, command higher trust scores in user perception studies, and maintain the strongest resale values in the aftermarket. While newer extensions like .ai and .io are gaining traction, .com remains the gold standard for serious businesses.


