How to Value A Domain Name
Did you make a speculative investment in a domain name some years back and are now wondering what it’s worth? In this article, domain name specialist Joe Uddeme provides expert insight into how to accurately value what you have in your portfolio.
How to Value A Domain Name
Valuations can be confusing whether you are the buyer or seller. “What’s my domain worth?” is a question that many owners ask themselves. “Why are domains so expensive?”, an intending buyer may ask after seeing the price of the asset they want.
Utilizing an appraisal services tool is crucial to accurately assess the value of certain names for various purposes, such as buying, selling, or evaluating brand name changes.
We will dive deep into domain valuation and the factors that affect the value of a domain, but first it’s helpful to understand why they cost money in the first place.
Key takeaways
Domain name values rise and fall as with other asset classes
Accurate domain name valuation ensures both buyers and sellers leave the negotiation table happy
Understand what makes one domain name more valuable than the next
Access evaluation tools to help you arrive at a fair price
Understanding Domain Value
Domain value is a crucial aspect of the online business world, and understanding it can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their digital assets. Remember, values could rise and fall according to market trends and the desirability of a name to a particular buyer at any point in time.
Knowing the value of a name is essential for both buyers and sellers, as it ensures fair transactions and helps in strategizing future investments.
In this section, we will delve into the concept of domain value, its importance, and the factors that influence it – as well as offer a complete review of the best-known domain appraisal services.
What is a Domain Worth?
Domain worth refers to the monetary value of a name. It’s an estimated amount that an asset could be sold for on the market. This estimated value is influenced by various factors, including the domain’s length, keywords, and extension.
Domain worth is a critical factor in determining the value of a business, as a high domain worth can significantly enhance a business’s overall value. For instance, a memorable and relevant name can attract more traffic, improve brand recognition, and ultimately lead to higher revenue.
Why Do Domain Names Cost Money?
A domain name is an online property – and property is not free. They are scarce by design; once a person buys an asset, it belongs to them as long as they pay the renewal fees. Likewise, it costs money to maintain the vast computing infrastructure that powers the internet, and selling digital domains is a way for registrars to recoup their costs.
Expertise in buying premium domains is crucial to ensure accurate appraisals and competitive pricing, helping buyers avoid over-payment.
Why Would You Need To Value A Domain?
It is important to have an estimate of what a name is worth, whether you are the buyer or seller for any potential sale. Understanding a domain’s worth ensures that a buyer won’t overpay for an asset and a seller won’t sell their domain for a price far below what they could have gotten from another acquisition partner.
Domain name valuation helps buyers or sellers assess the worth of a domain and pay or receive a fair market price.
What Makes An Asset Valuable?
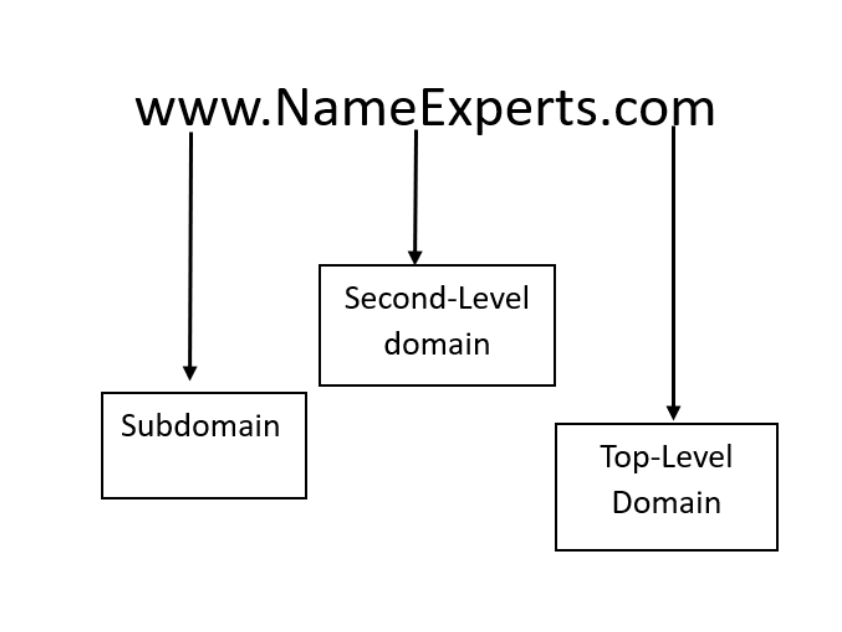
The Top-Level Domain (TLD)
The TLD refers to the last segment of a domain name that comes after the “dot” symbol (.com, .net, .ai, .co, .xyz, etc.). It plays a big role in the value of your asset due to supply and demand insight and data. For instance, .COM is the most popular option for buyers, so domains with this TLD tend to be more expensive than others with less interest. Some other TLDs also have a reputation for being expensive because of a strong market, like .ai and .io – according to current data.
Domain Length
The number of characters of an asset also affects its value metrics. The rule of thumb is that the lesser the number of characters, the more valuable the asset.
Number of Words
Similarly to length, the number of words in a name affects its valuation. The lesser the number of words, the more upside an asset has. This happens because domains with one or two words are easier to remember and thus command more brand power.
Age or Domain History
How long a domain has been owned by someone else contributes to its value. The longer the period of ownership, the higher the chances of that domain being recognizable. So, domains owned for a long time tend to command higher prices than new or short-lived ones.
Domain Popularity
If a name is already in use, the volume of the traffic on the site using it contributes to its value. High-traffic domains are more expensive because the new owner can leverage the existing traffic to drive eyeballs to their own website.
Likewise, if an existing asset has backlinks from other websites, it will command a higher price because backlinks improve search engine rankings and help generate organic traffic.
Understanding the domain marketplace is crucial for accurately estimating values and optimizing URL investments.
Availability of Alternative Domains
Can the purchaser find a similar asset elsewhere? (for instance Trucks.com > Trucks.co or Trucks.net or the .org). If the buyer can’t find a similar name somewhere else, then they may be more willing to pay a higher amount for it.
Market Interest and Characteristics
Market interest and characteristics are two essential factors that influence the names. Internet market interest refers to the level of interest in a name, which can be driven by trends, industry relevance, and the popularity of certain keywords.
Characteristics, on the other hand, refer to the attributes of the name, such as its number of characters, extension, and keyword density.
A URL with high market demand and desirable characteristics can command a higher price. For example, short, memorable domain names with popular extensions like .com are often more valuable sales due to their high demand and ease of recall.
How To Determine A Domain’s Value
There is no specific formula for this activity. However, there are some free tools and services to help you estimate the cost of a domain name.
1. Research Tools
The first step in figuring out how much a name can sell for is checking out the rate of similar domain names. Thus, you can use a research tool to see what similar domain names are selling for and compare them to your own. This will help you select a fair market price. Some sites are free to use while others charge a fee.
DN Journal is a good example of a platform that collates sales figures and displays them to readers for free.
Namebio, much like DN Journal does a great job cataloging recent names with an easy to use scan tool. They offered a monthly service fee for multiple inquiries.
Domain Name Wire is another free resource. You can find blog posts about notable domain sales to help you estimate what you can sell yours for.
Godaddy is a great resource to see what names may be available. They also offer a fast transfer service.
There are many others, but these a few good places to start.
2. Use An Appraisal Service
A domain appraisal service estimates the market value of a name. They appraise a domain based on many factors, including popularity, search engine ranking, social media shares, TLD, and by comparing it to similar domains.
These domain appraisal services platforms make it easy to get an educated answer on how much a domain is worth.
A free valuation tool can give you an overview of the appraisal value, such as godaddy.
3. Find Out What Others Are Willing To Pay
A more direct way to answer the question of “what is a domain worth?” is to understand the domain sales marketplace and see what others are willing to purchase it for. The easiest way to do this is to list your domain on a marketplace like Sedo and Afternic and see what offers you receive to purchase. Create cool landing pages to help drive leads. This data can help set better pricing. You can use the offers as the yardstick for valuing the domain.
Combining AI and Human Expertise
To accurately determine domain value, it’s essential to combine artificial intelligence (AI) and human expertise. AI searches can analyze vast amounts of data, including market trends, search volume, and similar domains, to provide an estimated value request. They are vast resources for information.
These automated tools can quickly process information and identify patterns that might not be immediately apparent. However, human expertise is necessary to interpret the data, consider the nuances of the domain name, and provide a more accurate appraisal.
Experienced domainers and brokers can offer insights that go beyond raw data, such as understanding the potential for future trends and the strategic value of a domain within a specific industry.
How To Increase Your Domain’s Value
There are several ways to boost the value of a domain, including:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
This refers to optimizing a web page such that it ranks high on search engines. You can do this by including relevant keywords in your niche and getting backlinks from other websites. If people can find your website on Google algorithms, they will click on it more often and give you higher conversions, which translates into a higher domain value when you analyze the data.
Market Your Site
You can advertise your website on appropriate venues like social media services, search engines, or even use free word of mouth for your Company. This lets people know you exist and will likely drive higher eyeballs to your domain, giving it a greater value.
Availability of Other Domains
People are less willing to pay a high price for a domain if they can get something similar for cheaper elsewhere, e.g., Cars.com > Cars.co. One way to avert this is to buy the keyword across multiple TLDs, e.g., Box.com, Box.org, Box.net, etc. This way, the intending buyer will have less leverage.
Build An Online Presence
You can create profiles on social media platforms to build an online presence. This gives your domain more brand power and, in turn, a higher evaluation figure.
Types Of Domain Name Valuations
There are three main types of domain name valuation:
Retail Pricing
These are domain names directly offered by the owners to end users with a clear use case. The end users already have something in mind to do with the domain, usually for a website, so are more willing to pay a higher sum than the estimates.
Liquid Pricing
This comes into play when domain names are being offloaded by an owner, court order, or a bankruptcy proceeding sales. The domains are typically sold as a group and are cheaper to buy because it is a fire sale. However, the chances of finding domains with liquid pricing estimates are slim compared to the others.
Liquid pricing is usually between 20% to 30% of retail pricing.
Investor Pricing
This is when domain names are offered for sale by professional domain brokers or flippers. You can find these types in an auction where you will likely bid against other people to acquire a domain. Some people may exchange domains with other Internet portfolio investors or team up to acquire a single valuable name for their domain portfolio.
Investor estimates pricing between 40% to 60% of retail pricing.
Working with Domain Investors and Brokers
Domain investors and brokers play a crucial role in the domain name market. They help individuals and businesses buy, sell, and appraise their names, leveraging their expertise to ensure fair and profitable transactions. Brokers, meanwhile, act as an expert go-between the buyer and seller of a domain name.
Role of Domain Investors
Domain investors are individuals or companies that buy and hold domain names with the intention of selling them at a profit. They often have a deep understanding of the domain name market and can provide valuable insights into the value of a domain name.
Investors typically maintain a domain portfolio as part of their business, which includes a variety of domain names that they believe will appreciate in value over time. By analyzing market trends and leveraging their experience, domain investors can identify undervalued domains and acquire them at a lower cost, with the aim of selling them at a higher price in the future.
About the author
Joe Uddeme is Director and Principal of NameExperts.com, one of the world’s leading domain name brokerage services. He has overseen domain name sales and acquisitions totaling more than $150 million and is renowned worldwide as a go-to expert in buying and selling premium domains. Contact us at: [email protected]