Learning how to buy a domain name is the essential first step in establishing any online presence. The process is straightforward once you understand how domain registration works, but making the wrong choices early — picking a weak name, skipping WHOIS privacy, or registering for only one year — can cost you time and money later. This comprehensive guide covers every scenario: how to buy a domain name on GoDaddy and other ICANN-accredited registrars, how to buy a domain name permanently by securing long-term registration, how to buy a domain name for email and professional branding, and what to do when the name you want is already taken or about to expire. Whether you are launching a startup, building a personal brand, or expanding an existing business, this article gives you a clear, actionable roadmap from first search to final setup.
Getting right down to basics, here’s NameExpert.com Director Joe Uddeme with our definitive guide to buying a domain name. Whether you’re a complete beginner or a would-be domain trader, it’s a great place to start.
A domain name is your website’s unique identifier. It is the address people type into their browser when they want to visit your website. For example, typing “nameexperts.com” in your browser leads to this very website.
Most businesses with an online presence need a domain name, but business owners sometimes don’t know how to get one. If you want to buy a domain name for yourself or your business, you’ve arrived at the right place.
Key Takeaways
- What to do before buying
- Choosing the right name and getting it registered
- Buying a domain owned by someone else
- What to do next
Before Buying Your Domain
Let’s examine the essential steps to take before buying a domain name:
Choose a domain name
A domain is a unique web address, meaning two websites can’t use the same domain name. The first step to buying a domain is to choose the right domain name for your business.
The domain should be brandable and easy to remember. It’s how customers will find you, so avoid any name that gives people headaches when trying to remember it.
The domain should preferably include the name of your business so that people can easily guess the address if they are not sure what it is. Let’s say you run an electronics store named MJ Gadgets; the perfect domain name is MJGadgets.com. If this domain isn’t available, you can look for alternatives like ShopMJGadgets.com, BuyMJGadgets.com, and MJGadgets.net.
Choose a premium domain name if you can afford it, as they are short, catchy, and memorable domain names that draw valuable organic traffic. Most successful online businesses use premium domain names.
Choose an Extension
The extension is what comes after the dot (.) in your domain name. “.COM” is the most popular domain extension and should be your first choice. If “.COM” isn’t available, you can pick alternative extensions like “.NET,” “.ORG,” and “.CO.”
Google and other search engines have confirmed that your choice of extension doesn’t impact rankings. However, it significantly affects consumer perception. People generally don’t trust uncommon domain extensions like “.XYZ,” “.BLOG,” “.WEBSITE,” etc.
Understand How Domains are Valued
Before making a final decision, you should understand how domain names are valued, especially if you plan to sell the domain later. Many factors contribute to a domain’s value, including:
- Length: The shorter a domain’s length, the easier it is to remember and the more valuable it becomes.
- TLD (top-level domain): Some domain extensions are more valuable than others, such as “.COM” “.NET,“ .AI,” “.IO,” etc. The more popular the domain extension, the more valuable it is.
- Length of domain history: The longer a domain name has existed on the web, the more likely it is to command a high value.
- Keyword popularity: Domains with generic keywords people frequently search for tend to have high value, e.g., “Amazon.com,” “Stripe.com,” “Square.com,” etc.
Verify if it is available
Considering the above factors, it’s time to check if your desired domain name is available. You can do this by simply going to any domain registrar and typing the desired name in the search box.
If the domain is available, the registrar will offer to sell it to you. Otherwise, the registrar will notify you that someone else has already registered the domain.
To demonstrate, let’s search for a random domain, “ournameexperts.com”, on Namecheap, a popular domain registrar. Namecheap said this domain name is available, and we could register it immediately.
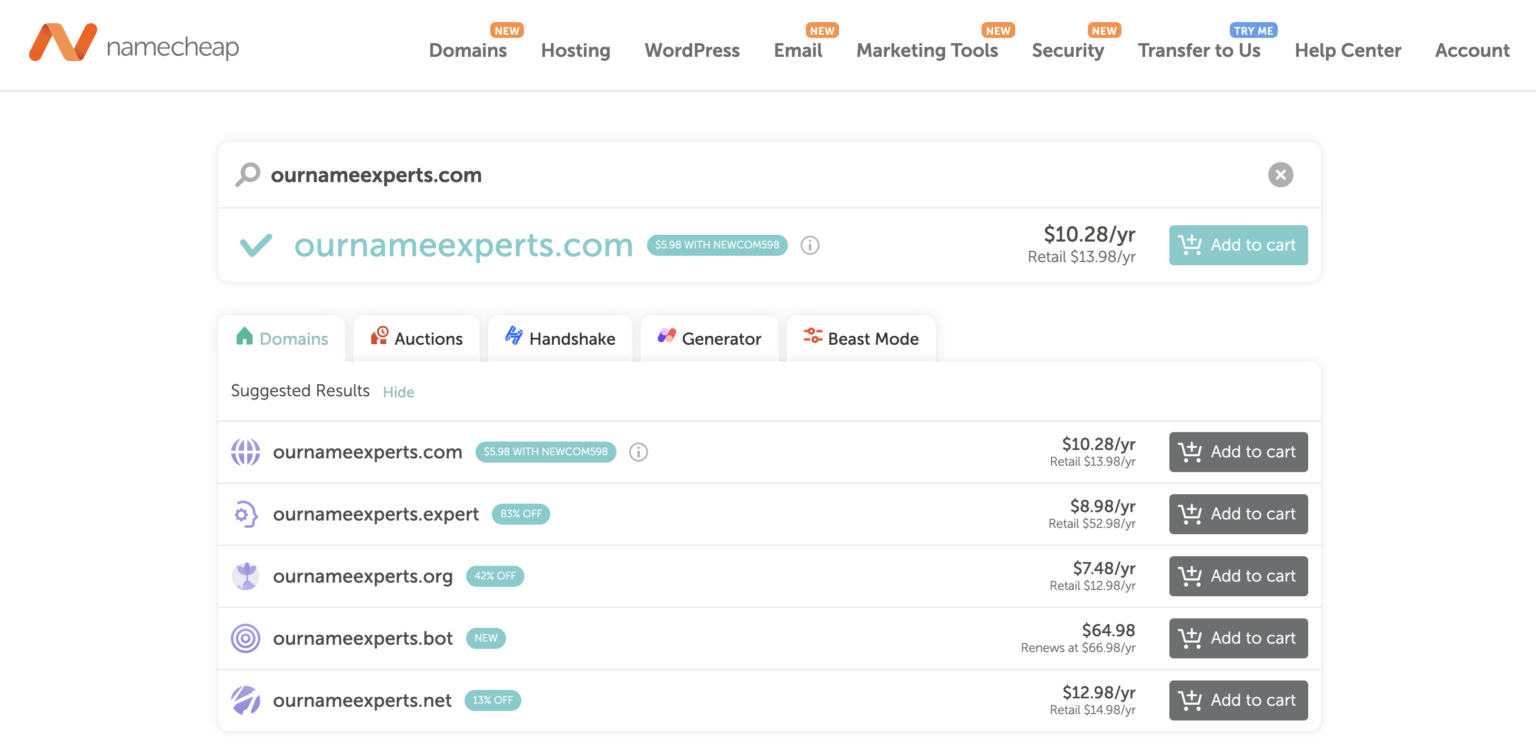
Now let’s search for “nameexperts.com.” Namecheap said this domain name has been registered by someone else since 2000. Of course, that’s the domain you’re currently on, so you can’t register it for yourself.
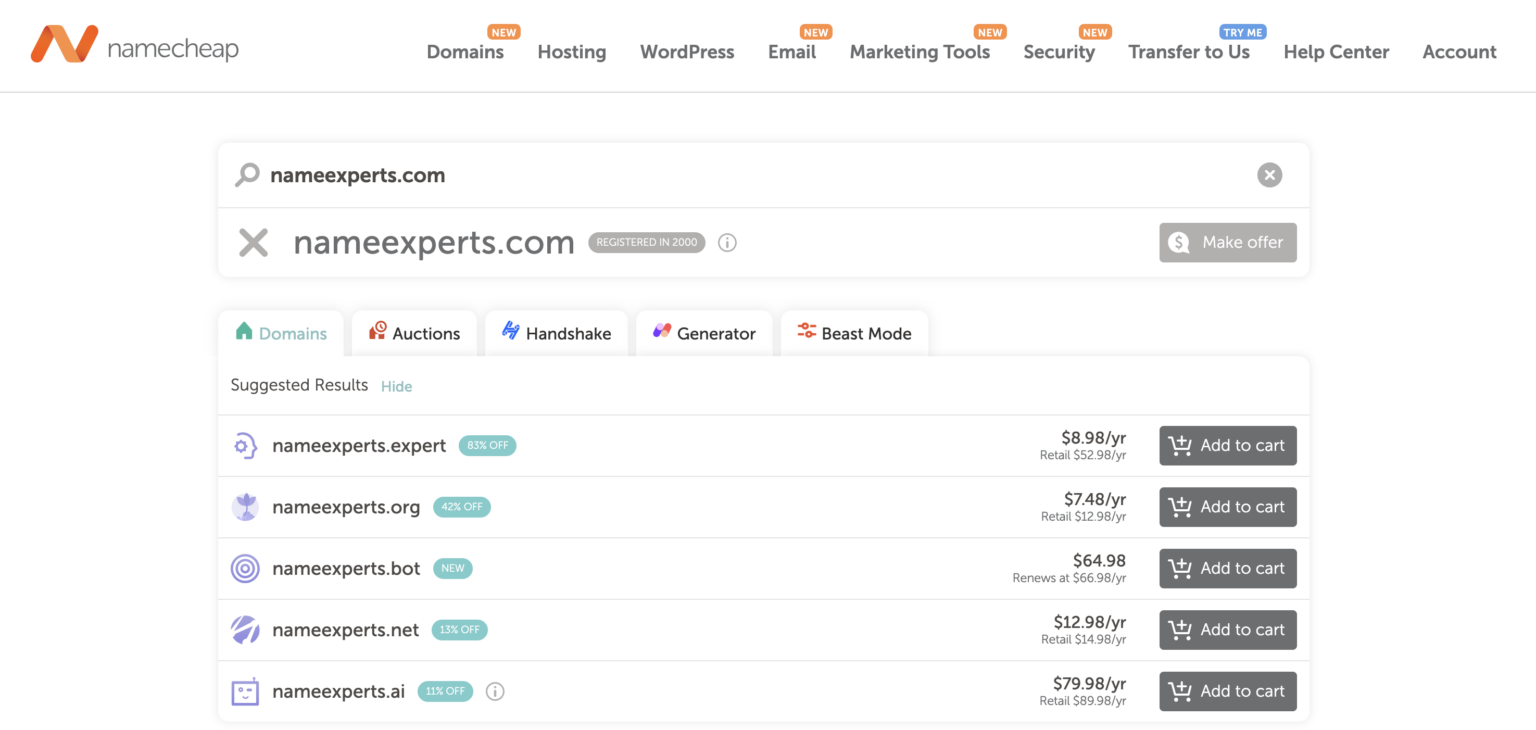
If your desired domain name is available, move to the next section on how to buy a domain name outright. If it has been taken, move to the ensuing section on how to buy a domain name that is already registered.
How to Buy a Domain Name
1. Choose a domain registrar
Any domain name must come from an accredited registrar, such as Namecheap, Dynadot, Hover, Bluehost, and Domain.com. Over 2,400 domain registrars are accredited by ICANN, the governing body of the global domain registration system, so finding a suitable one shouldn’t be an issue.
You can see the full list of all ICANN-accredited registrars here. Any supposed registrar not on this list is illegitimate.
2. Select your domain and extension
The next step is making a final choice about the domain and extension for your online business. We’ve discussed the factors that should influence your decision, but it’s worth reiterating that “.COM” is the best extension. This is the first extension most people consider when looking for a brand’s website.
If a random person wants to guess your website name, they’ll likely type the name followed by a .COM and hope their browser will show your website.
The .COM extension is easily recognizable and helps your website rank higher on search engines. Domain names with this extension also command a higher resale value, giving it a competitive edge over other domain extensions.
3. Select How Long to Register the Domain
Domain name ownership isn’t etched in stone. Every domain has an expiry date, although you can renew the registration for as long as you want. You can register a new domain for up to 10 years, with each additional year carrying higher upfront costs.
The bright side is that you don’t need to bother about short-term price changes once you’ve registered a domain for many years.
If you want to build a valuable long-term brand, 5 to 10 years is the optimal period to register a new domain. But if you can’t afford a long-term registration, you can register it for a year and turn on auto-renew so that the registrar automatically renews it when due.
You can’t technically buy a domain forever, but you can use some workarounds to own it for a seemingly infinite time.
4. Purchase your Domain
Enter the available domain name into your registrar’s search box and click the buy button. On the checkout page, most registrars suggest adding domain privacy to the registration package. Some registrars offer domain privacy for free, while others demand extra fees for this perk.
Do you need domain privacy?
Domain privacy protection means hiding your personal information from the public WHOIS database. This ICANN-operated database contains information on all domain owners and is open to anyone.
However, you might be uncomfortable with your contact information being out in the open. In that case, you can request domain privacy for your registrar to hide your personal details from the WHOIS database.
If you have no issues with your contact information being publicly searchable in the WHOIS database, you can ignore your registrar’s domain privacy suggestion.
5. Complete the Registration Process
Pay for the domain name with a credit or debit card and complete the registration process. Your registrar will ask for contact information, including a name and email address, to register the domain. This information is usually listed in the WHOIS database, but domain privacy lets you hide it.
6. Verify domain registration
Your registrar will send a verification email confirming ownership of the domain you purchased. Click on the link in the verification email and smile because you have formally joined the club of domain name owners.
How to Buy a Domain that is Already Registered
We can predict your disappointment if you find out that your desired domain has already been registered. However, don’t fret—there’s still a way out. You can contact the owner and formally offer to acquire their domain, especially if it isn’t connected to an active website.
Finding a domain owner and making a reasonable acquisition offer can be exhausting, so seeking a domain broker’s services is advisable. Domain brokers are experts who specialize in buying and selling domain names– the internet’s equivalent of a real estate agent.
If you’re interested in a house not publicly offered for sale, you’ll likely seek a real estate agent. Similarly, if you want a domain that is already registered, seek a domain broker to handle the negotiations.
Domain brokers can help you find the owner of a domain even if their information isn’t available on the WHOIS database. Then, they’ll reach out to the owner for negotiations.
This part is critical because domain brokers have proper knowledge and experience in domain name valuation. If you’re negotiating directly, you might underbid a domain and cause the owner to ignore you. Or you may overbid and get played. A domain broker sets a reasonable bid on your behalf and adjusts when necessary.
If the owner agrees to sell their domain name, the broker handles the escrow and ensures you aren’t cheated. Then, they’ll transfer the domain name to you.
Sometimes, the broker will explain that they have found the owner but they don’t want to sell for any reason. In that case, it’s wise to avoid beating a dead horse and seek a new domain name instead – preferably something similar to your first choice.
It can be as simple as choosing another extension – such as saying goodbye to OurNameExperts.com in favor of OurNameExperts.net.
One of the most important things we do for clients is advise them on domain name strategy. We have many years of experience in suggesting and sourcing valuable names that have incredible potential.

What to Do After Buying Your Domain
You’ve acquired a domain, so what’s next? A lot can happen. The obvious choice is to connect your domain to a website and work on attracting traffic.
You’ll need a web hosting plan from a reliable company. The company hosts your website on its servers so that people can access it anytime, and you’ll pay a fee for this perk.
The good news is that web hosting has become more affordable than ever– you can find hosting packages for as low as $5 monthly.
The type of website you want determines your hosting provider. For example, if you run an online store, you’ll need an e-commerce hosting service like Shopify, Shift4Shop, Squarespace, and WooCommerce for WordPress. If it’s a news site, social platform, booking website, or anything else, you can find endless hosting options for it.
You can also create a professional email address attached to your domain name. Professional email addresses make your business look brilliant and increase the chances of getting a response when you pitch to clients.
You can trademark your domain, market the website, and even sell it later. There are endless things to do after buying a domain name.
About the author
Joe Uddeme is Director and Principal of Name Experts, one of the world’s leading domain name brokerage services. He has overseen domain name sales and acquisitions totaling more than $150 million and is renowned worldwide as a go-to expert in buying and selling premium domains. Contact us at: [email protected]
Subscribe for More Domain Buying & Selling Advice
Get Expert Guidance on Your Domain Purchase
Choosing and registering the right domain name is one of the most important decisions for your brand. Whether you need help finding the perfect name, negotiating for a taken domain, or setting up hosting and email, our team is here to help.
Get Started TodayFrequently Asked Questions
Domain names cannot technically be purchased forever in a single transaction -- they are leased in renewable periods, typically ranging from one to ten years. However, you can effectively buy a domain name permanently by registering it for the maximum term your registrar allows (usually ten years), enabling auto-renewal with a valid payment method, and keeping your contact information up to date so you never miss a renewal notice. As long as you continue renewing before the expiration date, the domain remains yours indefinitely and no one else can claim it.
To buy a domain name on GoDaddy, visit their website and type your desired name into the search bar. GoDaddy will show you whether the exact .COM is available along with alternative extensions and similar name suggestions. Select the domain you want, choose your registration duration (we recommend at least five years), add WHOIS privacy protection, and complete checkout. The entire process takes less than ten minutes, and your domain is active almost immediately after payment is confirmed.
Yes, you can absolutely buy a domain name for email use only. After registering the domain through any accredited registrar, you connect it to an email hosting provider such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, or Zoho Mail by updating the domain's MX (Mail Exchange) records. This gives you a professional email address like [email protected] without requiring a live website. Having a custom domain email dramatically improves credibility with clients, partners, and prospects compared to using a free Gmail or Yahoo address.
When a domain name is about to expire and the current owner does not renew it, it goes through a grace period, a redemption period, and then drops back to the open market. You can buy a domain name that is expiring by placing a backorder through a drop-catching service such as SnapNames, DropCatch, or NameJet, which will attempt to register the domain on your behalf the instant it becomes available. Alternatively, some expiring domains are listed on auction platforms before they drop, giving you the opportunity to bid directly. Monitoring expiration dates through tools like ExpiredDomains.net or your registrar's alert system increases your chances of successfully acquiring the name.
To buy a domain name anonymously, you need to ensure your personal details do not appear in the public WHOIS directory or in any negotiation correspondence. Start by enabling WHOIS privacy protection (sometimes called Domain Privacy or ID Protection) at your registrar, which replaces your name, address, and email with those of a proxy service. If you are purchasing a taken domain, hire a domain broker to negotiate on your behalf so the seller never learns your identity or business name -- this also prevents the seller from inflating the price based on your perceived budget. Using a privacy-focused registrar like Njalla or Orangewebsite provides an additional layer of anonymity.
Once your domain purchase is confirmed, there are several critical steps to complete right away. First, verify that WHOIS privacy protection is active and enable registrar lock to prevent unauthorized transfers. Next, connect the domain to a reliable web hosting provider by updating the nameservers or DNS records, and set up professional email through a service like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365. Finally, consider registering the matching domain in other popular extensions (.NET, .ORG, common misspellings) to protect your brand, and begin the trademark registration process if the name is central to your business identity.


