
Domain Buying Guides
-
How to Buy a Domain Name
-
How to Buy a Domain Name Owned by Someone Else
-
Negotiating a Domain Price
-
What is a Premium Domain Name & Why You Should Buy One
-
How to Choose a Domain Name
-
How to Value a Domain Name
-
Domain Names for Startups
-
How to Buy a .com Domain Name
-
Things to Watch Out for When Buying a Domain
-
Domain Name Investing
-
Buy & Selling Domains
-
Best Domains to Buy
Name Experts provides premium
domain service to:
Escrow is important when buying domain names, especially those of high value. Domain name expert Joe Uddeme explains how domain name escrow works – and why you should use a domain escrow 3rd-party when making highly-priced acquisitions.
What is Domain Name Escrow?
Domain name escrow is a specialized service designed to protect both buyers and sellers during domain name transactions.
In this process, a neutral third-party agent holds the payment and domain information until all conditions of the transaction are met.
This setup ensures that the buyer receives the domain name and the seller gets their payment, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and deception.
By using domain name escrow services, both parties can enjoy a secure and efficient transfer of domain ownership, providing peace of mind throughout the transaction. A domain name consulting service can help make the process much easier.
What Is Escrow?
Escrow is an arrangement in which a neutral third party temporarily holds money meant for a purchase until specific conditions are met. The money will only be transferred to the intended recipient when the conditions are met.
If the conditions are not fulfilled, the money will go back to the buyer. In domain name and other transactions, the escrow process often involves a lawyer managing legal documents, ensuring compliance with laws, and securely holding the assets and money in a trust account until the terms of the agreement are fulfilled.

What Can Escrow Be Used For & Why
Escrow is common in transactions where a significant amount of money is involved, e.g., real estate. It is necessary to protect the buyer from losing money in case the seller does not fulfill the terms of the deal.
Domain transactions can be pricey, which makes escrow and other services necessary just like with real estate. After all, domain names are online real estate. Escrow protects against:
- Sellers refusing to deliver a domain despite agreeing to do so.
- Buyers refusing to pay for a domain despite an agreement to buy it.
- Payment being made – but the domain not being transferred to the buyer.
Secure payment is crucial in domain name transactions, and escrow services ensure that the financial exchange is safe and protected.
In short, escrow ensures that both parties in a deal stick to their agreed terms. It is a mediator of the transaction and refuses to complete it until both parties act in good faith.
How Does Escrow Work?
1. Agreement on price and deal
The buyer and the seller negotiate and agree on how much is to be paid for a domain name or group of domain names. They also negotiate important factors like the date of payment, method of payment, and what currency to use.
2. Buyer places agreement with an escrow company
With the deal terms drawn out, the buyer finds an escrow provider and deposits the payment with an escrow agent. Once the payment goes through, the buyer pays escrow company will notify the seller and tell them to transfer ownership of the domain name related to the escrow transaction.
3. Domain Name Is Transferred
The seller will transfer the domain name to the buyer. The wire transfer procedure varies depending on the domain registrar, but both parties will work together to ensure a smooth transfer.
It is crucial to involve legal counsel in domain transfers to secure the transaction and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
4. Domain Transfer Is Confirmed
After the domain is transferred, the buyer will notify the seller and agree with the escrow company that the seller has fulfilled their part of the deal.
5. Payment Given To Seller
With the domain transfer confirmed, the escrow company completes the escrow transaction by using a money order and sending the money deposited by the buyer to the seller.
What fees are associated with using an escrow service?
The escrow usually charges a commission on the value of the deal. Some may also charge a flat fee in addition to a commission. The exact commission may vary depending on the deal volume.
Benefits of Using Escrow For Buyers and Sellers
The benefits of using escrow for domain names include:
- Security: The escrow holds the money until all deal terms are fulfilled, so there are little chances of the buyer losing their money without getting the intended domain name. The buyer also feels more secure dealing with a trusted escrow company than with a stranger over the web. Additionally, escrow services safeguard domain transactions by holding funds and domain holder information, minimizing the risk of fraud.
- Assurance: The buyer is assured that they will get the domain they want, and the seller is assured of payment once the domain transfer is confirmed.
- Customer support: Escrow services usually offer customer support and can guide the buyer throughout the process of acquiring a domain name.

Choosing the Right Escrow Services
Selecting the right 3rd-party escrow provider for domain name transactions is crucial for a smooth and secure process. Start by looking for a reputable and licensed escrow company with a proven track record in handling domain name transactions.
Evaluate their fees and payment terms to ensure they fit within your budget. Additionally, consider the quality of their customer service and support, as this can be invaluable if any issues arise during the transaction.
A reliable escrow provider should offer a secure and transparent process to deposit funds, with clear contractual obligations and a well-defined escrow agreement. Research the company’s reputation online and read reviews from previous clients to ensure you are working with a trustworthy escrow company.
Domain Name Transfer and Intellectual Property
Transferring ownership of a domain name involves several steps and can be particularly complex when intellectual property rights are involved. A domain name can be considered intellectual property if it is trademarked, which can impact its value and transferability.
Before proceeding with a domain name transfer, it is essential to conduct a clearance search to ensure the domain name does not infringe on any existing trademarks.
Utilizing a domain name escrow provider can facilitate this process by ensuring that both parties fulfill their contractual obligations and that the domain name is transferred securely.
This helps protect best interests of the buyer and the seller, ensuring a smooth and legally compliant transfer of the domain name.
Alternatives To Using Escrow
Attorney
A licensed attorney can draft a sales contract that is legally binding for buyer and seller. If any party breaks the contract, they can be sued for damages in court.
The attorney can also act as an escrow organization and only transfer money from the buyer to the seller if the terms of the contract are fulfilled.
An attorney is crucial in selling domain names to ensure all legal aspects are covered, and the transaction is secure.
Domain marketplace
There are many marketplaces where you can acquire domain names. Here, the marketplace acts as a custodian of the domain and only the seller transfers it to the buyer after payment is confirmed, which is then given to the seller.
Best Domain Name Escrow Services
Escrow.com
Escrow.com is the world’s largest online escrow service, and it has specific features for domain sales. The buyer can initiate the escrow request and provide the seller’s contact information for Escrow.com to get in touch.
The buyer transfers the agreed sum to Escrow.com, and it is only when they confirm the domain has been successfully transferred that Escrow.com will disburse the money to the seller.
Escrow.com charges 3.25% for deals between $0 and $5,000; 0.89% for deals between $5,001 and $25,000; and $162.5 + 0.25% for deals over $25,001.
Sedo Domain Transfer Service
Sedo is a popular domain name and website marketplace, especially useful for those looking to buy or sell domain names.
Its domain transfer service puts it as a middleman between the buyer and the seller. Sedo receives the payment from the buyer and the domain name from the seller.
When both ends are confirmed, Sedo transfers the domain to the buyer and the buyer sends the money to the seller.
This service incurs a 3% fee on the domain purchase price, with a minimum of $60.
Afternic
Afternic is another popular domain name marketplace focused on high-value domains. It offers an escrow service to protect both the buyer and the seller.
Afternic holds the agreed amount and only disburses it to the former owner or seller when the buyer has confirmed receipt of the domain. If either party breaks the deal terms, the sale will be canceled and the money given back to the buyer minus the escrow fee.
The drawback here is that Afternic doesn’t charge escrow fees separately. It takes a 20% fee, which includes both sales and escrow commissions on all domains listed on its platform.
Using an Escrow Service
It is necessary to use an escrow service if you are paying a significant amount for a domain name and it helps protect you and the seller. If you need guidance in the domain buying process, including escrow, contact us for help.
We have negotiated over $150 million in domain name sales and have over a decade of experience in domain name buying and transfers.
About the author
Joe Uddeme is Director and Principal of NameExperts.com, one of the world’s leading domain name brokerage services. He has overseen domain name sales and acquisitions totaling more than $150 million and is renowned worldwide as a go-to expert in buying and selling premium domains. Contact us at: [email protected]
Subscribe for More Domain Buying & Selling Advice
Related posts


Top Domain Buy Services for 2025 – Expert Review
Working with an experienced domain name buyer can be one of the quickest and least stressful ways to secure the domain you need for your business. In this article, we’ll weigh up some of your best options. Before diving into our list, it’s essential to understand what domain buy services are. Domain name acquisition specialists (AKA domain buy services) are people (brokers) who act on your behalf to secure a domain name you wish to purchase. As well as being expert domain name negotiators, they are usually highly skilled at tracking down names that do not appear to be for sale. They have the expertise and experience to negotiate with domain owners – and can provide clear guidance on pricing, ensuring you don’t pay over the odds when purchasing a domain name. Our list contains many of the best-known domain buy services in the marketplace today and highlights some of their key points. The Role of a Domain Buyer Domain name buying services play a crucial role in bridging the gap between buyers and sellers. They are experts in the domain marketplace and usually bring long-established relationships and networks to the table. These networks can prove invaluable, especially when dealing with highly sought-after domains (also known as premium domain names). Moreover, buy-side brokers can often access exclusive listings that are not publicly available, giving you an edge when acquiring premium domains. The Negotiation Advantage One of the main advantages of using a domain broker is the negotiation skills they bring to the table. Domain buying experts are well worth having on your side if they are seasoned professionals or industry veterans who understand the nuances of domain value and market trends. They can communicate with domain owners to negotiate a fair price, often securing a deal that would be challenging – if not impossible – for someone without this expertise. This negotiation process shouldn’t be overlooked, especially when dealing with domains that have sentimental value or are held for speculative purposes. After all, domain names don’t have a ‘true’ value that is fixed: the prices they achieve reflect what somebody is prepared to pay at any given point in time. Streamlined Acquisition Process The domain acquisition process can be complex. It usually involves legal checks, valuation assessments, and secure payment transactions. Domain name buy services simplify this process by handling everything on your behalf. They ensure that all legal and financial aspects are managed correctly, which reduces the risk of potential pitfalls. Note: this process is often much more complex and drawn out than people sometimes realize. However, with skill and experience, seasoned domain buy service professionals will make each purchase as streamlined as possible.
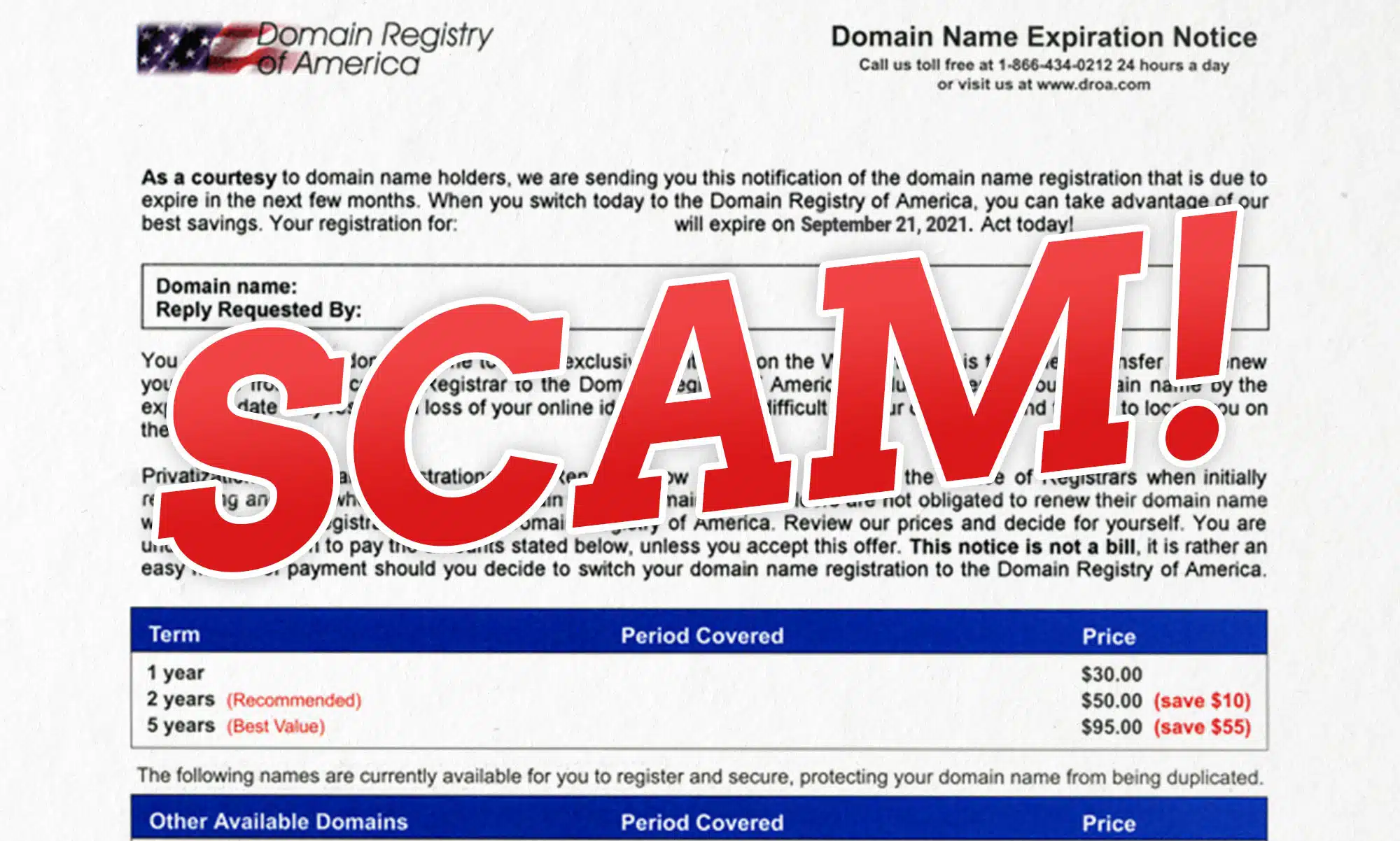
Understanding the Domain Name Scam
The bigger the domain name purchase price, the more attractive it is to scammers and fraudsters. Global domain name broker Joe Uddeme shares his top tips for staying safe when buying or selling premium domain names. It’s essential to understand the different types of domain name scams to protect yourself and your online identity. Domain name holders must be vigilant about renewing their domain names to retain exclusive rights. Domain name scams can be difficult to spot, but there are ways to identify them, such as recognizing phishing emails. One domain name renewal scam typically involves urgent phone calls or emails pressuring you to renew your domain names immediately and pay or risk losing your domain. This domain name renewal scam tries to trick people using phishing scams and deceptive tactics when registering names. Awareness and reporting are crucial to protect yourself. Be cautious of emails or letters that create a sense of urgency or threaten to cancel your domain name registration. Watch out for fraudulent domain renewal notices that may look official but are not. Domain registrations often come with options for renewal or transfer, so explore these to avoid falling for scams. Always verify the authenticity of the email or letter by contacting your registrar company directly. Be aware of deceptive practices by companies that send official-looking letters from a domain registry, urging you to transfer your registrations under false pretenses. Protecting Yourself from Domain Scams Always use a secure payment method to pay for domain name renewal. Recognizing legitimate renewal notices is essential to avoid unnecessary fees and potential loss of domain ownership for the customer, so don’t ignore every email you received about your names. Just treat them all with caution. Verify the authenticity of the email or letter by contacting your domain registrar company directly. Scammers often exploit the relationship with your existing registrar by suggesting that a transfer is merely a renewal process. Monitor your domain name registration and renewal dates to avoid missing important deadlines. Scammers use various methods, including urgent phone calls and deceptive emails, to execute a renewal scam. Use domain locking to prevent illegal transfers. Domain hijacking is another threat that can be mitigated by this measure. Registration scams typically manifest through fake renewal notices, creating confusion and unwarranted financial pressure. Keep your contact information private by using a domain name privacy service. Scammers may trick owners through fake offers, exploiting confusion around domain registration and renewal. Fraudulent phishing scams often target website owners, too, using tactics to deceive them into believing they owe money or need to make changes to their domain or hosting services. Understanding Domain Name Renewal Scams A Domain name renewal scam is a type of intellectual property scam or confidence scam that target the owner. These scams can result in financial loss for businesses and individuals. The financial loss can be substantial, affecting both small businesses and large corporations. Domain name scams can take many forms, including domain slamming, false offers to buy or sell domains, and fake trademark protection. It’s essential to understand the different types of domain name scams to protect yourself and your online identity. Domain Registry of America is an example of a fake trademark protection service. They contact the website owner claiming to have a trademark right or warning that someone else owns the rights to your name. Check your expiration date and make sure your domain information is protected so you don’t lose control of your asset. While you can’t technically buy a domain name forever, you can register and renew for extended periods. Domain name scams often involve unscrupulous domain name registrars attempting to generate revenue by tricking businesses into buying, selling, listing, or converting a domain name. These scams can be difficult to spot, but there are ways to identify scam tactics. Be cautious of emails or letters that create a sense of urgency or threaten to cancel your domain name registration. Always verify the authenticity of the email or letter by contacting your registrar company directly. Be able to recognize scammer tactics by paying attention to blog post and article updates. Customers should also consider adding two-factor authentication for all registered accounts, or hiring a domain name consultant for guidance. Definition of domain name scams A domain name scam is a fraudulent scheme where scammers deceive individuals or businesses into paying for fake registration services, overpriced renewals, or by impersonating legitimate registrars. It often involves phishing, domain hijacking, or misleading offers to trick victims into making unauthorized payments or losing control of their domain Importance of awareness and prevention Awareness is the first line of defense against domain name scams. The website owner must be vigilant and proactive in protecting their assets. This means being cautious of unsolicited offers, verifying the authenticity of emails and letters, and keeping domain registration information up to date. By understanding the risks and taking preventative measures, website owners can safeguard themselves from getting scammed. Regularly monitoring domain status and using secure payment methods for renewals are also crucial steps in prevention. Domain Registry and Scams Domain renewal scams: fake notices and invoices Domain scams are a common tactic used by the scammer to trick the owner into paying for unnecessary services or transferring their site to a different registrar. These scams typically involve sending fake notices or invoices that claim the domain name is due for renewal. Often involving inflated prices, notices often appear to be from a registry or a legitimate company, but they are actually from fraudsters posing as an internet registry. Swindlers use various tactics to make these notices or invoices appear legitimate. They may include the domain owner’s contact information and registration details, creating a sense of urgency by claiming that the domain names will expire or be lost if the renewal fee is not paid immediately. They may ask for you to renew your domain and pay an exorbitant fee. This pressure can lead the holder to act hastily without verifying the authenticity of the notice or link. They may also try an inflated price on the renewal scam for your website or use a scare tactic and tell you your name is about to expire if you don’t pay a fee. To avoid domain scams, website owners should be cautious of unsolicited notices or invoices. Always verify the authenticity of the sender by contacting the current registrar directly or checking the domain name holders registration information online. Domain Scams – How to Stay Safe To protect yourself from domain scams, it’s crucial to be vigilant and take proactive steps. Here are some tips to help you avoid falling victim to domain scams: Keep your domain registration information valid, up to date and secure so it never expires. Simply renewing ahead of time. Set a calendar reminder to be a step ahead Be cautious of emails or letters that create a sense of urgency or threaten to cancel your domain name registration. Verify the authenticity of the email or letter by contacting your domain registrar or reseller directly. Use secure payment methods when you register and renew your site or domain name. Avoid Mail that contains your physical mail address. Address customer concerns by contacting customer support. Monitor your domain name registration and renewal dates to avoid missing important deadlines. Consider adding auto-renew as a double check for registering your asset before it expires. Use domain locking to prevent unauthorized transfers of your registered assets. Keep some money in the registrar account in case you have an issue with your credit card when you pay. Keep your contact information private by using a domain name privacy or proxy mail service. By following these tips, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to domain scams and protect your online website identity for your domains. Reporting Domain Scams to Your Domain Registrar If you suspect that you have been a victim of a domain scam, it’s essential to report it to the relevant authorities. Here are some steps you can take: Report the scam to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). Share the information about the scam on social media to warn others. Use the social media links provided to share the post. Report the scam to your domain registrar company such as Network Solutions. Contact the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) Complaint department and let them know about the letter or email. File a complaint with the Better Business Bureau (BBB) if the scammer is a business. By reporting domain scams, you can help prevent others from falling victim to the same scam and bring the fraudsters to justice. About the author Joe Uddeme is Director and Principal of Name Experts, one of the world’s leading domain name brokerage services. He has overseen domain name sales and acquisitions totaling more than $150 million and is renowned worldwide as a go-to expert in buying and selling premium domains. Contact us at: [email protected]
Why Work with Name Experts
Name Experts offers personalized domain brokerage services, assisting clients in buying or selling premium domain names with expert appraisal, negotiation, and complete transaction management while ensuring confidentiality.
Some of our most
successful stealth acquisition and sales
